Dealing with the Antimalware Service Executable causing high CPU can be a challenging yet solvable issue. Throughout this article, we’ve explored the causes and provided a range of solutions to mitigate this common problem.
By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your computer’s performance, ensuring that it runs more efficiently. Remember, regular maintenance and staying informed about your system’s operations are key to a smooth computing experience.
In this article:
ToggleWhat is Antimalware Service executable
The Antimalware Service Executable, also known as MsMpEng.exe, is a core process of Windows Defender, which is the built-in antivirus and antimalware software in Windows. This process plays a crucial role in Windows Defender’s functioning. Here’s a bit more detail about what it does:
- Real-Time Protection: The Antimalware Service Executable is responsible for continuously scanning your computer for malware and other threats. It operates in the background, checking files, connections, and other relevant data to ensure your computer’s safety in real-time.
- System Scanning: Aside from real-time protection, this service also executes scheduled or manual scans of your system. This includes full system scans or quick scans, depending on your settings or actions.
- Threat Definition Updates: It helps in downloading and installing the latest threat definitions. These updates are essential for the software to recognize new viruses and malware.
- Background Operations: The service is responsible for various background operations related to security, such as monitoring system activities for suspicious behavior and checking downloaded files.
While this service is crucial for system security, it can sometimes use a significant amount of system resources, especially CPU and memory. This is particularly noticeable during full system scans or when updating its threat definitions.
If you find that the Antimalware Service Executable is consistently using a high amount of CPU or memory, it could be due to frequent real-time scanning or an issue within Windows Defender itself. In such cases, some users consider alternative antivirus solutions or tweak Windows Defender’s settings to mitigate the impact on system performance.
How to fix Antimalware Service executable causing high CPU usage
In case the Antimalware Service executable causes high CPU usage on your Windows PC, try some of the solutions we listed below.
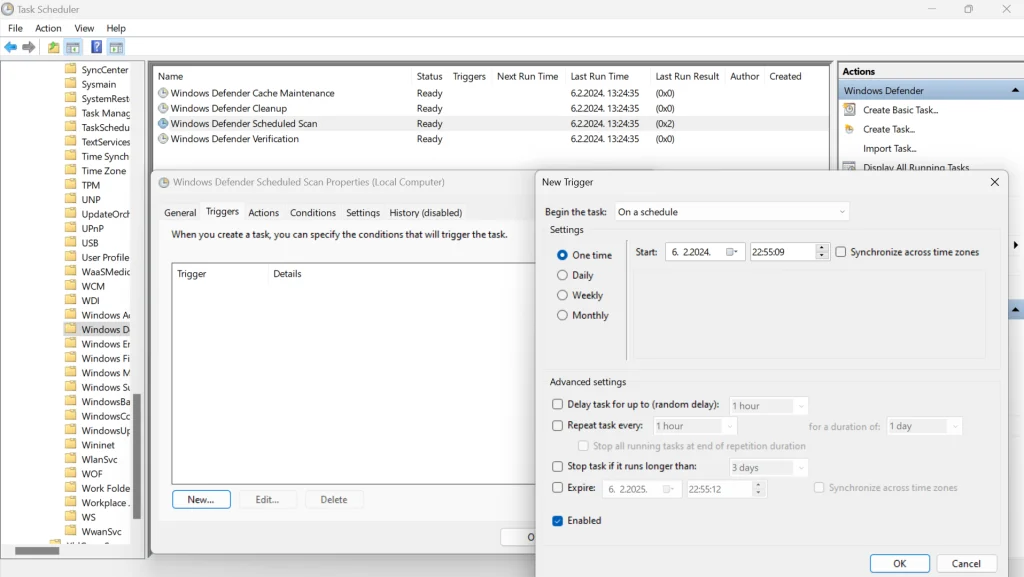
Solution 1: Change Windows Defender’s Schedule
Modifying the schedule for Windows Defender can help reduce its impact on system performance by running scans at times when you’re less likely to feel the performance hit.
Here’s how to change Windows Defender’s schedule:
- Open the Task Scheduler.
- Navigate to Library/Microsoft/Windows/Windows Defender.
- Right-click on Windows Defender Scheduled Scan and select Properties.
- Go to the Triggers tab and adjust the schedule to a time when you are less likely to use your PC.
Solution 2: Add Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender Exclusion List
By adding the Antimalware Service Executable process to the exclusion list of Windows Defender, you can reduce its CPU usage, as it won’t scan its own process.
Here’s how to add it to the exclusion list:
- Open Windows Security.
- Navigate to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Scroll down and select Add or remove exclusions.
- Click on Add an exclusion, select Process, and type
MsMpEng.exe, which is the name of the Antimalware Service Executable.
Solution 3: Check for Malware
Sometimes, malware can cause Windows Defender to use more resources. Running a full system scan can detect and remove any threats.
Here’s how to run a full system scan for malware:
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & threat protection.
- Click on Scan options and select Full scan.
- Click on Scan now and wait for the scan to complete.

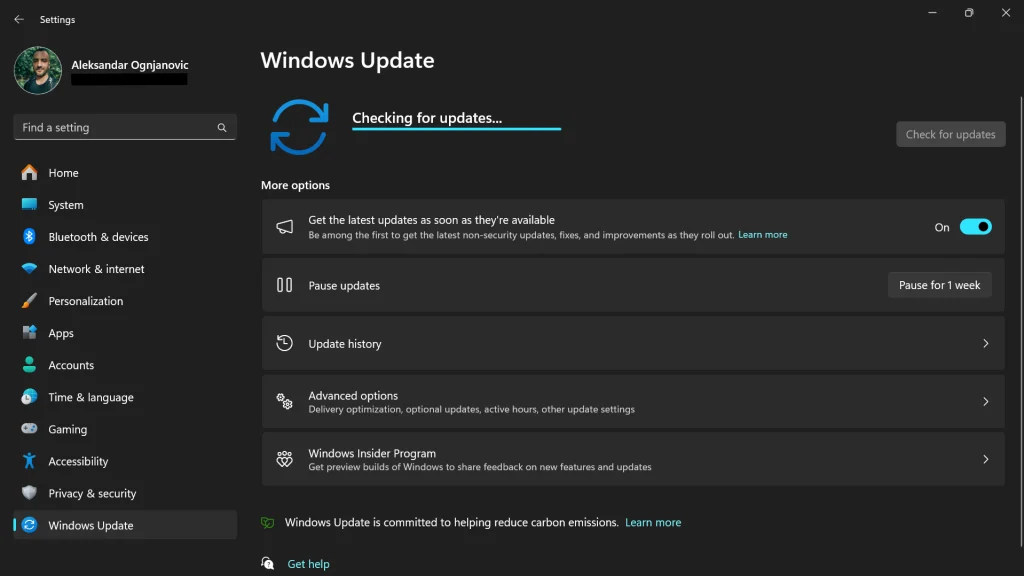
Solution 4: Update Windows
Ensuring that your Windows is up to date can also help, as updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes.
Here’s how to update Windows:
- Open Settings.
- Go to Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click on Check for updates and install any available updates.
Solution 5: Use a Different Antivirus Program
If the problem persists, you might consider using a different antivirus program. However, this means you’ll have to disable Windows Defender.
Here’s how to use a different antivirus program:
- Choose and install a reputable antivirus program.
- This should automatically disable Windows Defender. If it doesn’t, you can disable it manually in Windows Security > Virus & threat protection settings.
Solution 6: Disable and Re-enable Real-Time Protection
Temporarily disabling Real-Time Protection in Windows Security can help reduce CPU usage. However, be cautious as this will temporarily lower your system’s defenses against malware.
Here’s how to disable and re-enable Real-Time Protection:
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Toggle Real-Time Protection off and then on again.
Solution 7: Reschedule Windows Defender Scans
Adjusting the schedule for Windows Defender’s scans can help distribute the load to less busy times.
Here’s how to reschedule Windows Defender scans:
- Open Task Scheduler.
- Navigate to Library/Microsoft/Windows/Windows Defender.
- Modify the schedule for tasks like Scheduled Scan, Cache Maintenance, Cleanup, and Verification to times when your PC is less busy.
Solution 8: Use Third-Party Antivirus Software
Switching to a third-party antivirus program, such as Malwarebytes, AVG, or Bitdefender, can be an effective way to resolve high CPU usage issues caused by the Antimalware Service Executable. When you install third-party antivirus software, Windows Defender typically gets disabled automatically.
This action stops the Antimalware Service Executable from running and thus can reduce the CPU usage. Remember, it’s important to ensure you’re using a reliable and trusted antivirus program to maintain your system’s security.
Solution 9: Disable Windows Defender
For those who need to disable Windows Defender, it can be done via the Registry Editor or Local Group Policy Editor. However, proceed with caution as this action can leave your system vulnerable to threats if not replaced with another security solution.
Here’s a more precise way to disable Windows Defender using the Group Policy Editor:
- Type
gpedit.mscin the search bar and press Enter to open the Local Group Policy Editor. - Navigate to
Computer Configuration>Administrative Templates>Windows Components>Windows Defender Antivirus. - Double-click on
Turn off Windows Defender Antivirus. - Select
Enabledto disable Windows Defender, then clickApplyandOK.
Solution 10: Update Device Drivers
Updating device drivers is essential for optimal system performance and can be done directly through Windows. This method ensures you’re getting the correct drivers from the hardware manufacturer, which can reduce the risk of system instability and conflicts.
Here’s how to update device drivers the right way:
- Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager.
- Expand the categories and look for devices with a yellow exclamation mark, which indicates driver issues.
- Right-click on the device and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for updated driver software and follow the on-screen instructions to install any available updates.
- Repeat this for each device that needs an update.
Updating drivers via Device Manager ensures that you’re getting the correct drivers, but it’s always good to regularly check the manufacturer’s website for the latest driver updates, especially for key components like the graphics card and motherboard.
Dealing with the Antimalware Service Executable consuming high CPU can be a challenging yet solvable issue. Throughout this article, we’ve explored the causes and provided a range of solutions to mitigate this common problem.
By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your computer’s performance, ensuring that it runs more efficiently. Remember, regular maintenance and staying informed about your system’s operations are key to a smooth computing experience.
If you continue to experience issues, seeking professional assistance is always a wise decision. Keep your PC healthy and your computing experience optimal by staying vigilant about such issues.