The error code 0x80080005 in Windows, which is frequently encountered during update attempts, indicates a critical issue that prevents the operating system from applying required updates. This error, which is frequently caused by permission conflicts, corrupted update components, or system file discrepancies, can halt system upgrades and security patches, leaving your system vulnerable.
To resolve this error, a multifaceted approach is required, with a series of troubleshooting steps aimed at identifying the root causes. This article outlines comprehensive solutions for navigating and resolving the 0x80080005 error, including using built-in troubleshooting tools, manually resetting system components, and adjusting permissions.
In this article:
ToggleHow to solve the error “0x80080005” in Windows
The error code 0x80080005 frequently appears in Windows update processes, indicating that the system is unable to access or process the required updates. This could be due to a variety of factors, including service configuration issues, corrupted system files, or permission settings.
Here are some effective ways to address and resolve the error 0x80080005:
Solution 1: Reset Windows Update Components
Manually resetting the Windows Update components can resolve issues blocking updates.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator by searching for it, right-clicking, and selecting Run as administrator.
- Stop the BITS, Windows Update, Cryptographic, and MSI Installer services by typing and executing the following commands:
- net stop bits
- net stop wuauserv
- net stop appidsvc
- net stop cryptsvc
- Rename the SoftwareDistribution and Catroot2 folders to reset the update history by typing and executing:
- ren %systemroot%\SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.old
- ren %systemroot%\System32\catroot2 catroot2.old
- Restart the services you stopped earlier by typing and executing:
- net start bits
- net start wuauserv
- net start appidsvc
- net start cryptsvc
Solution 2: Check for System File Corruption
Corrupted system files can hinder update processes. The System File Checker (SFC) and Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tools can find and fix corrupted files.
- Run Command Prompt as Administrator.
- First, execute the DISM tool command:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth.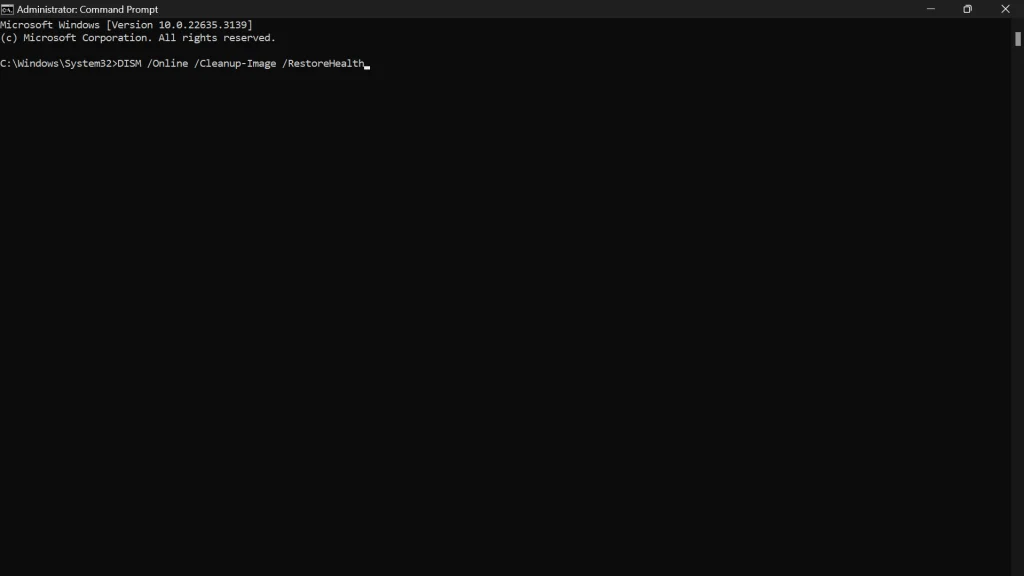
- After DISM completes, run the SFC tool by typing:
sfc /scannow.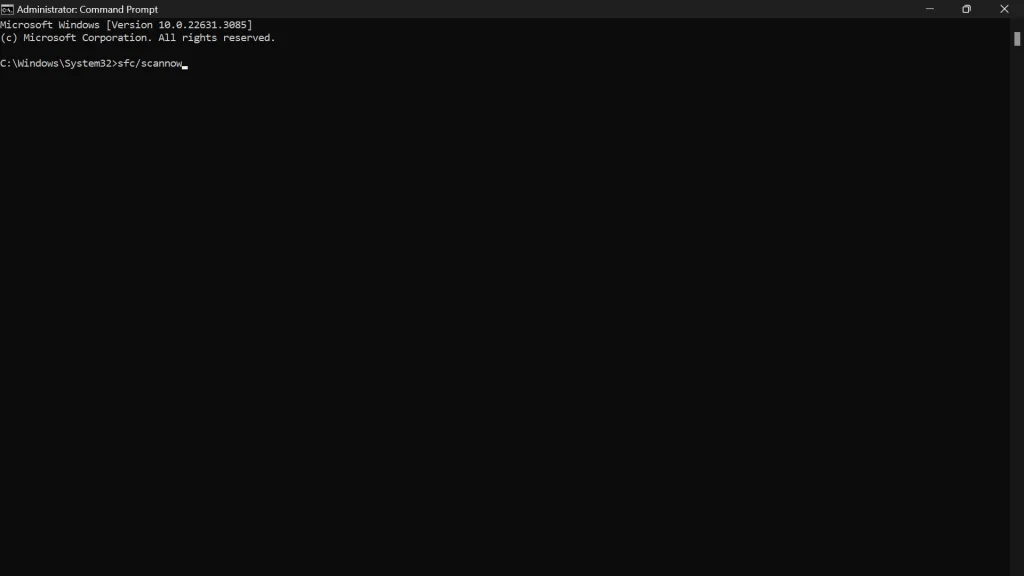
Solution 3: Adjust User Permissions
Insufficient permissions can sometimes cause update errors.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator and type:
net user administrator /active:yesto enable the built-in Administrator account. - Log out from your current account and log in as the Administrator.
- Attempt to run Windows Update again. Afterward, disable the Administrator account for security by running:
net user administrator /active:noin Command Prompt as Administrator.
Solution 4: Temporarily Disable Antivirus Software
Third-party antivirus software can occasionally block Windows Update. Temporarily disabling your antivirus might resolve this issue.
- Disable your antivirus software temporarily from its application settings.
- Try running Windows Update again. Remember to re-enable your antivirus software afterward.
You can also try getting and installing the update manually by downloading it from Microsoft Update Catalog.
Solution 5: Modify Registry Settings
Incorrect registry settings can contribute to update errors. Modifying specific registry keys can help, but be cautious as incorrect changes can significantly affect system stability.
- Open Registry Editor by typing
regeditin the Start menu and pressing Enter. - Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System.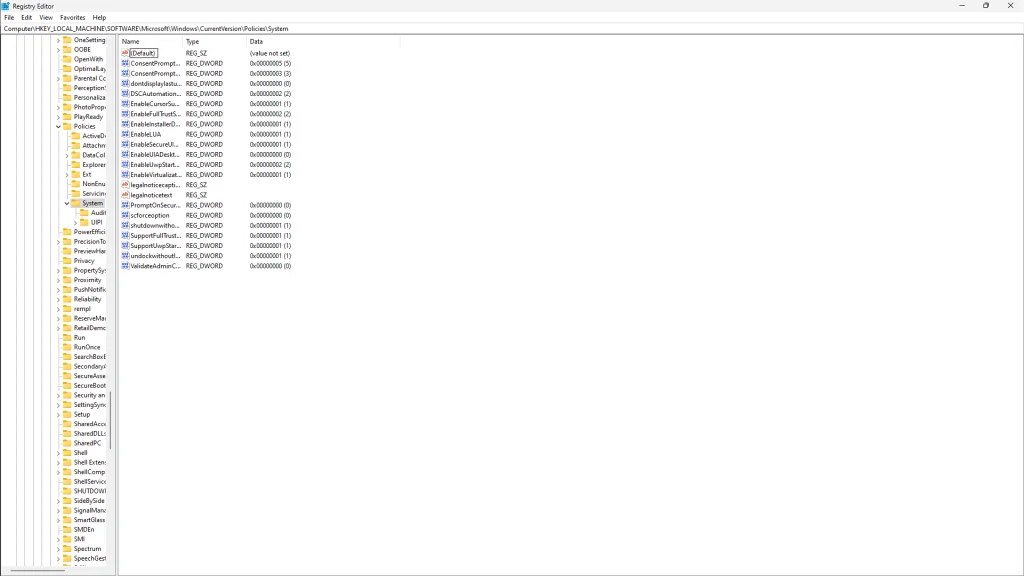
- Locate or create a DWORD value named
LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicyand set its value to1. - Restart your computer and attempt the update again.
Navigating the complexities of the 0x80080005 error requires a thorough understanding of Windows’ update mechanisms and the potential roadblocks that can occur within them. You can overcome the barriers to successful system updates by methodically applying the solutions provided, which range from using the Windows Update troubleshooter and resetting update components to taking ownership of critical system directories.
These steps not only address the immediate error, but also improve your system’s ability to handle future updates more smoothly. Regular maintenance, such as checking for updates and ensuring system files are intact, is critical in avoiding similar issues.
If the error persists despite these efforts, it may indicate a deeper systemic issue, necessitating professional assistance to ensure your system’s stability and performance.


