When it comes to optimizing your Windows PC, understanding the role of key system files can be crucial. Among these is hiberfil.sys, a file deeply intertwined with the hibernation feature of your computer. This file might not be widely known, but it plays a pivotal role in how your computer manages power and memory. The first step in optimizing your system’s performance and freeing up valuable disk space involves understanding what is hiberfil.sys and the specific function it serves.
In this article, we delve into the essence of the hiberfil.sys file, explaining its role in storing your session data when your computer enters hibernation mode. This feature, while useful for resuming work quickly and saving energy, can consume a significant portion of your hard drive space, especially in systems with large amounts of RAM.
We’ll explore how hiberfil.sys affects your computer’s storage and provide you with detailed steps on how to manage this file effectively. Whether you’re aiming to reclaim disk space or optimize your hibernation settings, understanding and managing hiberfil.sys is a key step.
In this article:
ToggleWhat is hiberfil.sys file in Windows 11
Hiberfil.sys is a Windows system file that plays a crucial role in the hibernation feature of your computer. When you put your computer into hibernation mode, unlike a standard sleep mode where the session is stored in RAM (thus requiring a small amount of power), hibernation mode saves the contents of your RAM to your hard drive. This is where hiberfil.sys comes into play.
This file essentially acts as a storage reserve for all the data that your RAM holds at the moment of hibernation. It includes all your open documents, running applications, and ongoing system processes. The primary purpose of this file is to ensure that when you turn your computer back on, you can resume exactly where you left off, with all your previously open applications and documents in the same state as when you hibernated the system.
The size of hiberfil.sys is typically comparable to the amount of RAM in your computer. For instance, if you have 16 GB of RAM, the hiberfil.sys file will also be around 16 GB in size. This one-to-one correspondence is necessary because the file must store an exact snapshot of your RAM. This size can be substantial, especially on systems with a large amount of RAM, leading to significant disk space usage.
Now, understanding this, you can manage the hiberfil.sys file better based on your usage and needs. If you rarely use the hibernation feature, disabling it can recover a substantial amount of disk space. On the other hand, if you frequently use hibernation for its convenience and energy-saving benefits, you might opt to adjust the settings or accept the space trade-off.
How to free up space by managing the hiberfil.sys file
If you find that you rarely or never use the hibernation feature on your Windows computer, you might be sitting on a potential opportunity to free up significant disk space. The hiberfil.sys file, while crucial for hibernation, can occupy an amount of space roughly equal to your RAM, which is particularly substantial in systems with higher memory.
If hibernation isn’t part of your regular computer usage, disabling it and thereby removing the hiberfil.sys file can recover valuable disk space, allowing your system to breathe a little easier. Here’s how you can do that:
Disabling Hibernation
If you find that you don’t use the hibernation feature or prefer to free up disk space, disabling hibernation is a straightforward solution. This will remove the hiberfil.sys file from your system, thus freeing up the space it was using.
Here’s how to disable Hibernation:
- Open Command Prompt with administrative privileges as described in the previous steps.
- Enter the command powercfg /hibernate off and hit Enter. This command disables the hibernation feature, and as a result, Windows will automatically delete the hiberfil.sys file.

Enabling or Disabling Fast Startup
Fast Startup is a feature in Windows that combines elements of a cold shutdown and the hibernate feature to allow for faster startup times. This feature also uses the hiberfil.sys file. Depending on your preference for boot speed versus disk space, you may choose to enable or disable this feature.
Here’s how to manage Fast Startup:
- Type “Control Panel” in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Go to “Hardware and Sound” and then “Power Options“.
- Click on “Choose what the power buttons do” on the left-hand side.
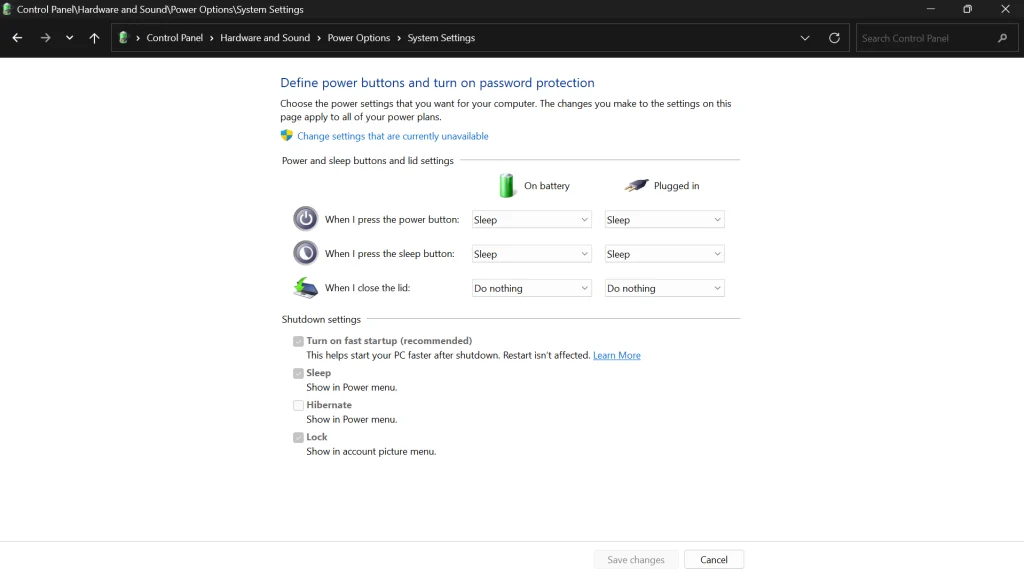
- Click on “Change settings that are currently unavailable“.
- Here you can check or uncheck “Turn on fast startup” to enable or disable this feature. Remember that disabling it might increase boot times but will free up disk space used by hiberfil.sys.
Understanding and managing the hiberfil.sysfile is crucial for Windows users who are keen on optimizing their system’s performance and disk space usage. Whether you choose to disable hibernation to recover disk space or adjust settings for a faster startup, each action plays a significant role in how your computer operates.
It’s about finding the right balance that works for your specific needs and usage patterns. Remember, like any system modification, it’s important to consider the trade-offs between convenience, performance, and available resources.
By following the steps outlined in this article, you can make informed decisions about managing hiberfil.sys, ensuring your Windows system runs efficiently while aligning with your personal or professional computing requirements.