The message “The file is too large for the destination file system” can stall your workflow, especially if you’re attempting to transfer enormous files. This recurrent problem is caused mostly by the restrictions of the FAT32 file system, which does not support files larger than 4GB.
Fortunately, there are several ways to get around this restriction, ranging from changing the file system on your storage device to splitting or compressing the huge file. This article presents simple solutions to overcome this barrier, allowing you to transfer large files efficiently and without data loss.
In this article:
ToggleHow to deal with the “The file is too large for the destination file system” error in Windows
The error “The file is too large for the destination file system” usually appears when attempting to transfer a file greater than 4GB to a device formatted with the FAT32 file system, which has a maximum file size limit of 4GB. Here are the best possible solutions to this problem:
1. Convert the File System to NTFS or exFAT
NTFS and exFAT file systems support larger file sizes. Converting your drive from FAT32 to NTFS or exFAT can resolve the issue without losing data.
To convert to NTFS:
- Back up your data as a precaution.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type
convert X: /fs:ntfs(replaceX:with the letter of your drive) and press Enter.
Note: Converting to exFAT is not directly supported via a simple command like NTFS and typically requires formatting, which erases all data on the drive. Use exFAT for drives that need to be compatible with both Windows and macOS.
2. Split the File into Smaller Parts
If converting the file system isn’t an option, consider splitting the large file into smaller parts using file compression software like 7-Zip or WinRAR.
- Install and open your chosen file compression software.
- Select the file to split, choose to compress, and select the option to split the file into parts smaller than 4GB.
3. Compress the File if you get The file is too large for the destination file system error
Compressing the file can reduce its size, potentially bringing it under the 4GB limit. To compress a file, right-click the file and select Send to > Compressed (zipped) folder. This will create a ZIP file. If the file size is still too large for the destination file system, consider using more advanced compression options in software like 7-Zip.
4. Format the Drive to exFAT or NTFS
If you don’t need the drive to remain in FAT32 and don’t have data to preserve on it, formatting it to NTFS or exFAT is a straightforward solution. Here’s how to format the Drive to exFAT or NTFS:
- Back up any important data from the drive.
- Open File Explorer, right-click the drive, and select Format.
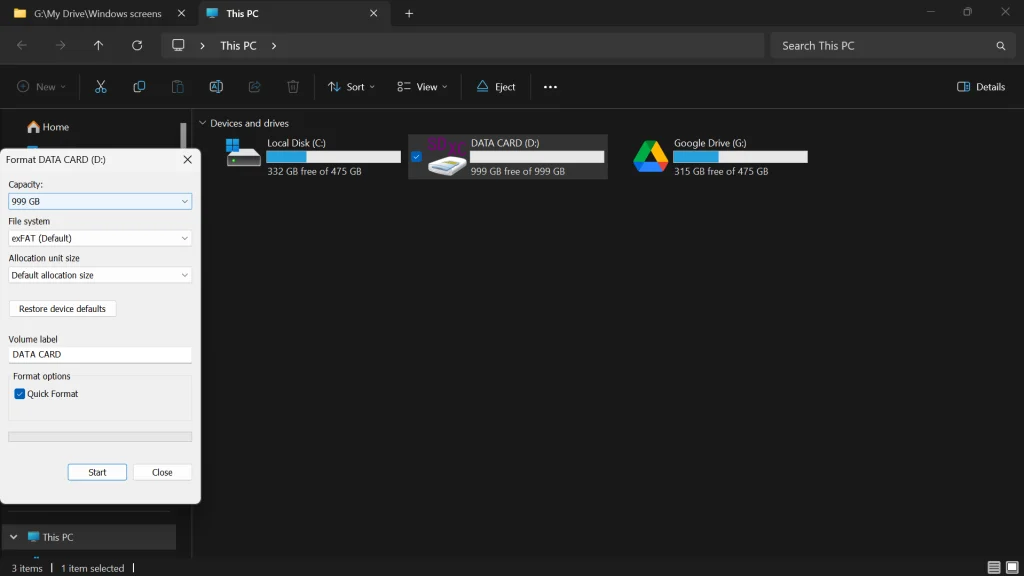
- Under File System, choose NTFS or exFAT.
- Click Start and follow the prompts to format the drive.
5. Use Cloud Services or Network Transfers
For situations where reformatting the drive or altering the file isn’t practical, leveraging cloud services or network transfers presents a reliable alternative. Cloud storage services like Google Drive, OneDrive, or Dropbox can easily handle large files, bypassing the limitations of your local file system. Similarly, a direct network transfer between computers on the same network can move large files without encountering the FAT32 size limit.
To use cloud services:
- Choose a cloud service and create an account if you don’t already have one.
- Upload your large file to the cloud. This process may take some time, depending on your internet speed.
- Once uploaded, you can access or download the file from any device connected to the internet.
For network transfers:
- Ensure both computers are connected to the same network.
- Share the folder containing your large file from the source computer. Right-click the folder, select Give access to > Specific people, and follow the prompts to share it on the network.
- On the destination computer, access the shared folder through the network and copy the file.
Additional Tips
- Choosing Between NTFS and exFAT: NTFS is ideal for internal drives due to its support for larger files and security features. exFAT is better for flash drives and external hard drives, especially if they need to be used with both Windows and macOS.
- Data Backup: Always ensure your important data is backed up before performing operations like formatting or converting the file system.
- Check Drive for Errors: Sometimes, file system errors can cause issues. Use the “Check Disk” utility (chkdsk) to scan and fix file system errors.
Fixing the “The file is too large for the destination file system” error is critical for users who frequently work with huge files. You can discover a good solution that meets your demands by looking at possibilities such as switching the file system to NTFS or exFAT, compressing the file, or even using cloud services for transfer. You can make some space on the drive with Microsoft PC Manager.
These approaches not only let you avoid the FAT32 system’s 4GB file size limit, but they also improve your file management skills. Implementing these solutions will make the process of transferring large files a seamless part of your digital routine, allowing you to focus on your work without being interrupted.